
Key Insight:
-
Waking up from sweat repeatedly throughout the night disrupts your sleep and leads to fatigue and irritability during the day.
-
Lack of restful sleep caused by night sweats impacts your productivity, concentration, and overall well-being at work.
-
Night sweats make you feel self-conscious about sweating excessively during sleep, causing discomfort and embarrassment, especially when you share a bed with a partner.
Sweating is a super intellectual body mechanism if you think about it. When our body gets too hot due to physical activities or high temperatures, the brain triggers the sweat glands to produce sweat. As sweat evaporates from our skin, it cools the body, bringing the temperature down to a comfortable level. Additionally, sweating also contributes to the elimination of toxins and waste products from the body, so we can stay in good health and well-being.
However, waking up drenched in sweat in the middle of the night is a whole different story. These nighttime episodes of excessive sweating, known as night sweats, can be disruptive and concerning for both individuals and their bed partners.
Night sweats go beyond the body's natural temperature regulation and can be linked to underlying health issues. The discomfort sweats cause can significantly affect sleep quality and overall well-being. If you find yourself sweating excessively during sleep, it's essential to seek answers and solutions to regain peaceful and restorative sleep.
What Causes Night Sweats?
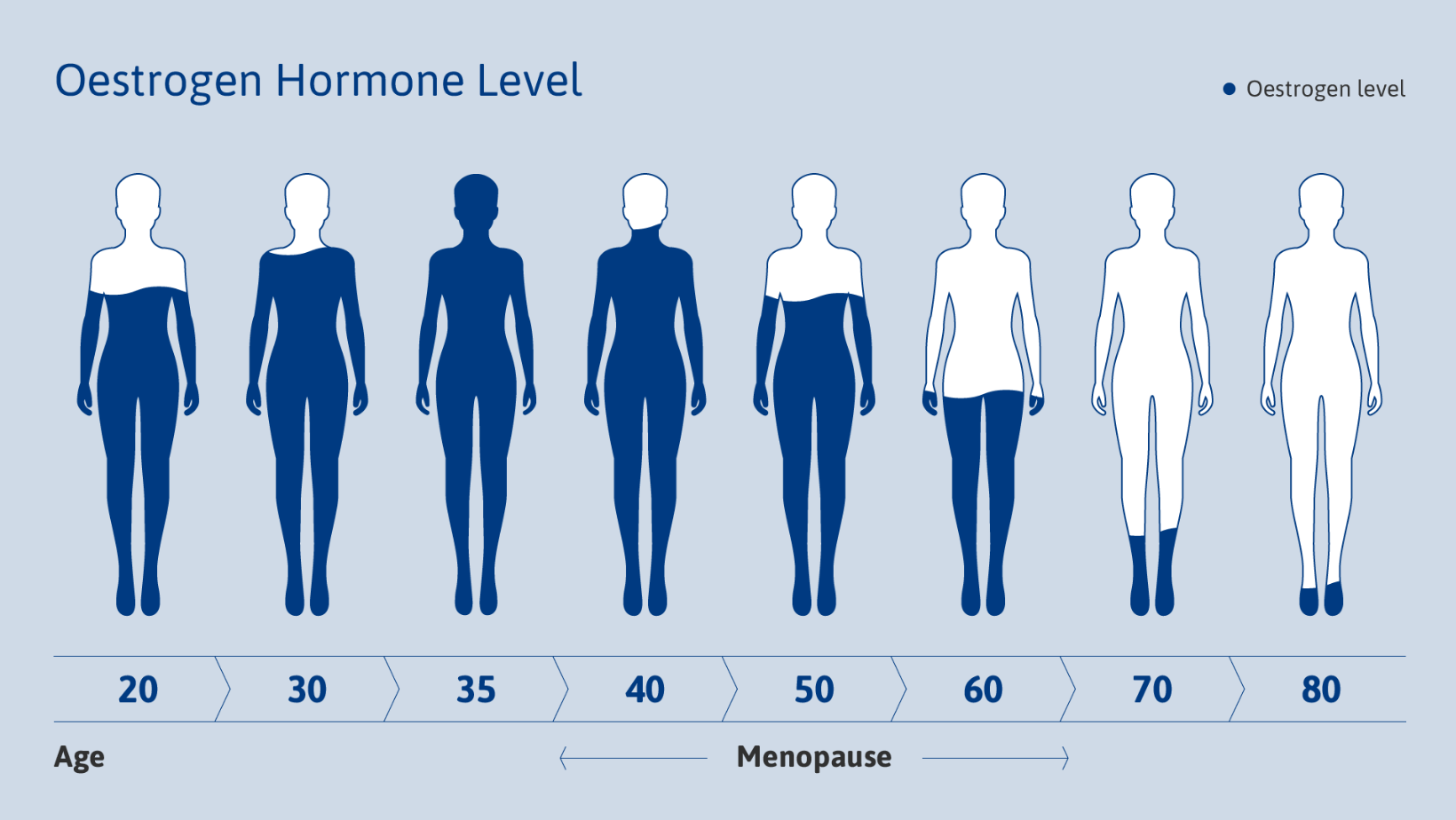
Night sweats can be caused by various factors, ranging from benign to more serious underlying conditions.
Menopause: Night sweats are a common symptom experienced by women going through menopause. Hormonal changes during this period can lead to hot flashes and night sweats as the body's internal thermostat fluctuates.
Hot flashes: These sudden episodes of intense heat and flushing usually begin in the perimenopausal phase and may continue even after menopause, affecting up to 60% of women. Lasting for a few minutes and occurring multiple times a day, hot flashes can also disrupt sleep when they happen at night, leading to night sweats.
Infections: Certain infections, such as tuberculosis or HIV, can cause night sweats as the body's immune system responds to the infection. Fever and night sweats often occur together in these cases.
Medications: Some medications, like antidepressants, hormone treatments, and fever-reducing drugs, may list night sweats as a potential side effect. These medications can disrupt the body's natural temperature regulation.
Anxiety and Stress: Emotional stress and anxiety can trigger the release of adrenaline, leading to increased body temperature and night sweats.
Sleep Environment: An overheated sleep environment, such as sleeping in a hot room or using heavy bedding, can contribute to excessive sweating during the night.
Medical Conditions: Night sweats can be a symptom of various medical conditions, such as hyperthyroidism, diabetes, or certain types of cancer. These conditions can cause hormonal imbalances and disrupt the body's natural cooling mechanisms.
What is Considered a Normal Amount of Sweating During the Night?
Pallavi Suyog Uttekar, MD, a board-certified clinician in human physiology, has stated, "While there is a wide range in how much people sweat, in general, the average person sweats between 0.5-2 liters an hour during physical activity. But according to some studies, people may lose a minimum of 3 liters a day, even without moving around all that much.”
When sleeping below 85 degrees at night, you should be sweating the least. However, your body still loses moisture through breathing and evaporation from the skin, known as insensible perspiration. This process doesn't involve the sweat glands. On average, a healthy young male loses around 25 milliliters of water per hour, or 200 milliliters over eight hours of sleep. Much of this moisture is simply exhaled and not absorbed by the mattress.
When You Need to Be Concerned About Night Sweats?
The timing for addressing your night sweats can vary depending on the individual. However, it is generally considered abnormal to lose more than one liter of sweat per night while sleeping. If you're unsure about how much one liter of sweat is, imagine waking up with completely drenched sheets and pajamas. Night sweats can be caused by a variety of factors, in addition to the ones mentioned earlier, such as eating spicy food or taking a hot shower. Sometimes, the direct cause may not be immediately apparent. Therefore, it's important to take note of any recurring night sweating conditions, as they may indicate potential health concerns and prompt you to seek professional assistance.
How to Stop Night Sweats and Get Better Sleep?

Change your daily routine
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and reduce the risk of dehydration-related night sweats.
Avoid Spicy Foods: Spicy foods can trigger night sweats in some individuals. Limit their intake, especially close to bedtime.
Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Reduce consumption of caffeine and alcohol, especially in the evening, as they can contribute to night sweats.
Manage Stress: Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation to manage stress, which can exacerbate night sweats.
Limit Electronic Use: Reduce exposure to screens before bedtime to improve sleep quality and reduce the likelihood of night sweats.
Keep everything cool
Optimize Your Sleep Environment: Keep your bedroom cool, well-ventilated. When the weather gets hot, consider using a fan and AC.
Dress Lightly: Wear lightweight, breathable sleepwear made from fabrics to help keep your body cool. Sleepwear made out of natural fibers like cotton, linen, and bamboo are usually good choices.
Use Moisture-Wicking Bedding: Use a cooling mattress topper or bed sheets to regulate body temperature. These beddings are usually made out of moisture-wicking fabrics, which are specially designed textiles that have the ability to draw sweat away from the skin and quickly move it to the fabric's outer surface where it can evaporate more easily. These fabrics are typically made from synthetic fibers like polyester, nylon, or spandex, and they are engineered to have hydrophobic properties, meaning they repel water and allow air to flow through the fabric.
If your symptom is severe
Seek Medical Advice: If night sweats persist despite lifestyle changes, consult a healthcare professional to identify and address any underlying medical conditions.
Discuss Medications: If you are taking any medications, inform your doctor, as certain medications can cause night sweats as a side effect. Your doctor may need to adjust your medication or explore alternative options.
Consider Hormonal Therapy: If night sweats are caused by hormonal imbalances, consult a healthcare professional to discuss hormone replacement therapy options.
Explore More
- How to Relieve Back Pain After Work and During Sleep? Solution from the Experts in 2023
- Yellow Stains on Your Mattress? Here's How to Clean and Disinfect for a Healthier Sleep
- How to Protect Your Mattress If You Enjoy Sleeping with Your Pets?





























